-
[spring boot] 연락처 관리 프로젝트 (+TDD)Server/Spring 2020. 4. 26. 21:23
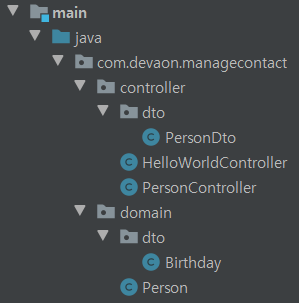
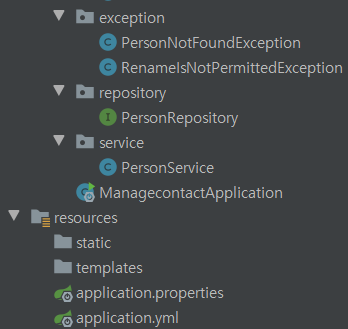
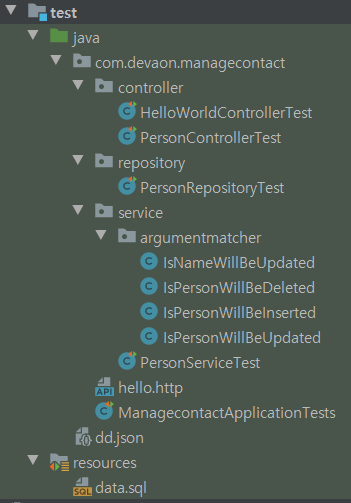
✔ 프로젝트 구조
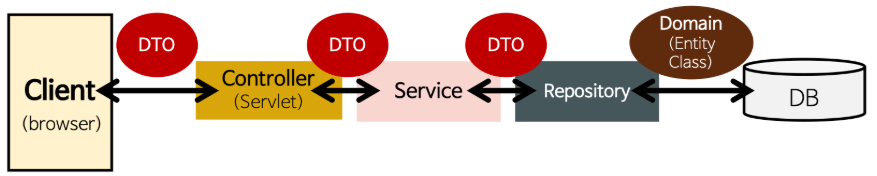
**✔MVC 패턴 (Model–View–Controller)**
**✔프로젝트 전체 코드 ( 깃허브 )**
👉👉👉 https://github.com/devAon/SpringBoot-Manage-Contact
✔ 프로젝트 코드 및 구현 내용 설명
build.gradle
dependencies { implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web' compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok' annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok' implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa' implementation 'com.h2database:h2' testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test' testImplementation 'org.junit.platform:junit-platform-launcher:1.5.0' testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.5.0' testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine:5.5.0' testImplementation 'org.mockito:mockito-junit-jupiter' }
** Domain **
- 실제 DB의 테이블과 매칭될 클래스
Person
@Entity @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @RequiredArgsConstructor @Data @Where(clause = "deleted = false") public class Person { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; @NonNull @NotEmpty @Column(nullable = false) private String name; private String hobby; private String address; @Valid @Embedded private Birthday birthday; private String job; private String phoneNumber; @ColumnDefault("0") private boolean deleted; public void set(PersonDto personDto) { if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(personDto.getHobby())) { this.setHobby(personDto.getHobby()); } if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(personDto.getAddress())) { this.setAddress(personDto.getAddress()); } if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(personDto.getJob())) { this.setJob(personDto.getJob()); } if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(personDto.getPhoneNumber())) { this.setPhoneNumber(personDto.getPhoneNumber()); } if (personDto.getBirthday() != null) { this.setBirthday(Birthday.of(personDto.getBirthday())); } } }@Entity
DB에 저장하기 위해 유저가 정의한 클래스. Domain
RDBMS에서 Table을 객체화 시킨 것
테이블과 연결될 클래스임을 나타냄
@Id
primary key를 가지는 변수 선언
@GeneratedValue
PK의 생성 규칙을 나타낸다.
기본값은 AUTO로 MySql의 auto_increment와 같이 자동증가하는 정수형 값
스프링부트 2.0 이전에는 자동으로 auto_increment가 됐지만
스프링부트 2.0 이후부터는 @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.Identity) 옵션을 줘야 auto_increment가 된다.
@Column
@Column에서 지정한 변수명과 DB컬럼명 다르게 주고 싶은 경우
(@Column(name=" ") 사용)
해당 어노테이션을 사용하지 않으면 기본적으로 멤버 변수명과 일치하는 DB컬럼을 매핑한다.
기본값 외 추가로 변경이 필요한 옵션 변경 가능. 예를들어 VARCHAR(255) -> VARCHAR(500) 수정
@NotNull : CharSequence, Collection, Map orArray의 객체가 null일 수 없다. 그러나 empty는 가능하다.
@NotEmpty :CharSequence, Collection, Map orArray의 객체가 null과 empty 값(size > 0)이 될 수 없다
@NotBlank: 'String'이 null일 수 없으며, legnth가 0보다 커야 한다.
@NoArgsConstructor
기본 생성자 자동 추가
옵션으로 access - AccessLevel.PROTECTED를 주면 기본생성자의 접근 권한을 protected로 제한할 수 있다.
Entitiy 클래스를 프로젝트 코드상에서 기본생성자로 생성하는 것은 막되,
JPA에서 Entity 클래스를 생성하는 것은 허용하기 위해 사용
@Getter
클래스 내 모든 필드의 Getter 메소드를 자동생성
@Builder
해당 클래스의 빌더패턴 클래스를 생성
생성자 상단에 선언시 생성자에 포함된 필드만 빌더에 포함
** DTO **
PersonDto
DTO(Data Transfer Object) 란?
dto package
- 계층간 데이터 교환을 위한 객체(Java Beans)이다.
즉, DB에서 데이터를 얻어 Service나 Controller 등으터 보낼 때 사용하는 객체이다.- Request와 Response용 DTO는 View를 위한 클래스이다.
**🐥참고 : VO (Valaue Object ) vs DTO**
👉 VO : 특정한 비즈니스 값을 담는 객체 👉DTO : 계층간 통신 용도로 오고가는 객체@Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor(staticName = "of") public class PersonDto { @NotBlank(message = "이름은 필수값입니다") private String name; private String hobby; private String address; private LocalDate birthday; private String job; private String phoneNumber; }*🐥참고 : Entity 클리스와 DTO 클래스를 분리하는 이유 *
- View Layer와 DB Layer의 역할을 철저하게 분리하기 위해
- Entity 클래스 : 테이블과 매핑되기 때문에 변경시, 여러 클래스에 영향을 끼치게 된다.
- DTO 클래스 : View와 통신하는 클래스로 Request, Response 는 자주 변경된다.
👉 따라서 분리해야한다.
** Repository (=DAO) **
DAO(Data Access Object) 란?
Repository package
- 실제 DB에 접근하는 객체로 DB에 data를 CRUD하는 계층인 Persistence Layer이다.
- Service와 DB 연결고리
ORM인 JPA를 사용하여 ( extends JpaRepository<Person, Long> ) 개발했다.
PersonRepository
public interface PersonRepository extends JpaRepository<Person, Long> { List<Person> findByName(String name); @Query(value = "select person from Person person where person.birthday.monthOfBirthday = :monthOfBirthday") List<Person> findByMonthOfBirthday(@Param("monthOfBirthday") int monthOfBirthday); @Query(value = "select * from Person person where person.deleted = true", nativeQuery = true) List<Person> findPeopleDeleted(); }PersonRepositoryTest
@Transactional @SpringBootTest class PersonRepositoryTest { @Autowired private PersonRepository personRepository; @Test void findByName() { List<Person> people = personRepository.findByName("tony"); assertThat(people.size()).isEqualTo(1); Person person = people.get(0); assertAll( () -> assertThat(person.getName()).isEqualTo("tony"), () -> assertThat(person.getHobby()).isEqualTo("reading"), () -> assertThat(person.getAddress()).isEqualTo("seoul"), () -> assertThat(person.getBirthday()).isEqualTo(Birthday.of(LocalDate.of(1991, 7, 10))), () -> assertThat(person.getJob()).isEqualTo("officer"), () -> assertThat(person.getPhoneNumber()).isEqualTo("010-2222-5555"), () -> assertThat(person.isDeleted()).isEqualTo(false) ); } @Test void findByNameIfDeleted() { List<Person> people = personRepository.findByName("andrew"); assertThat(people.size()).isEqualTo(0); } @Test void findByMonthOfBirthday() { List<Person> people = personRepository.findByMonthOfBirthday(7); assertThat(people.size()).isEqualTo(2); assertAll( () -> assertThat(people.get(0).getName()).isEqualTo("david"), () -> assertThat(people.get(1).getName()).isEqualTo("tony") ); } @Test void findPeopleDeleted() { List<Person> people = personRepository.findPeopleDeleted(); assertThat(people.size()).isEqualTo(1); assertThat(people.get(0).getName()).isEqualTo("andrew"); } }
*Controller *
PersonController
- 사용자의 요청이 진입하는 지점이다.
- 요청에 따른 처리를 결정한다.
- 사용자에게 view를 응답으로 보내준다.
@RequestMapping(value = "/api/person") @RestController public class PersonController { @Autowired private PersonService personService; @GetMapping("/{id}") public Person getPerson(@PathVariable Long id) { return personService.getPerson(id); } @PostMapping @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED) public void postPerson(@RequestBody @Valid PersonDto personDto) { personService.postPerson(personDto); } @PutMapping("/{id}") public void modifyPerson(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody PersonDto personDto) { personService.modify(id, personDto); } @PatchMapping("/{id}") public void modifyPerson(@PathVariable Long id, String name) { personService.modify(id, name); } @DeleteMapping("/{id}") public void deletePerson(@PathVariable Long id){ personService.delete(id); } }PersonControllerTest
@SpringBootTest @Transactional class PersonControllerTest { @Autowired private PersonRepository personRepository; @Autowired private ObjectMapper objectMapper; @Autowired private WebApplicationContext wac; private MockMvc mockMvc; @BeforeEach void beforeEach() { mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders .webAppContextSetup(wac) .alwaysDo(print()) .build(); } @Test void getPerson() throws Exception { mockMvc.perform( MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/api/person/1")) .andExpect(status().isOk()) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.name").value("aonee")) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.hobby").isEmpty()) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.address").isEmpty()) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.job").isEmpty()) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.phoneNumber").isEmpty()) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.deleted").value(false)); } @Test void postPerson() throws Exception { PersonDto dto = PersonDto.of("aonee", "programming", "seoul", LocalDate.now(), "programmer", "010-1111-2222"); mockMvc.perform( MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/api/person") .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8) .content(toJsonString(dto))) .andExpect(status().isCreated()); Person result = personRepository.findAll(Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC, "id")).get(0); assertAll( () -> assertThat(result.getName()).isEqualTo("aonee"), () -> assertThat(result.getHobby()).isEqualTo("programming"), () -> assertThat(result.getAddress()).isEqualTo("seoul"), () -> assertThat(result.getBirthday()).isEqualTo(Birthday.of(LocalDate.now())), () -> assertThat(result.getJob()).isEqualTo("programmer"), () -> assertThat(result.getPhoneNumber()).isEqualTo("010-1111-2222") ); } @Test void modifyPerson() throws Exception { PersonDto dto = PersonDto.of("aonee", "programming", "seoul", LocalDate.now(), "programmer", "010-1111-2222"); mockMvc.perform( MockMvcRequestBuilders.put("/api/person/1") .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8) .content(toJsonString(dto))) .andExpect(status().isOk()); Person result = personRepository.findById(1L).get(); assertAll( () -> assertThat(result.getName()).isEqualTo("aonee"), () -> assertThat(result.getHobby()).isEqualTo("programming"), () -> assertThat(result.getAddress()).isEqualTo("seoul"), () -> assertThat(result.getBirthday()).isEqualTo(Birthday.of(LocalDate.now())), () -> assertThat(result.getJob()).isEqualTo("programmer"), () ->assertThat(result.getPhoneNumber()).isEqualTo("010-1111-2222") ); } @Test void deletePerson() throws Exception { mockMvc.perform( MockMvcRequestBuilders.delete("/api/person/1")) .andExpect(status().isOk()); assertTrue(personRepository.findPeopleDeleted().stream().anyMatch( person -> person.getId().equals(1L))); } private String toJsonString(PersonDto personDto) throws JsonProcessingException { return objectMapper.writeValueAsString(personDto); } }Controller에서
-return 값이 void인 경우(post, modify, delete)에는assertThat, assertAll을 통해 검증을 한다.
뿐만 아니라, Repository값을 가져와DB값을 통해 검증한다.
-return 값이 있는 경우(get) 에는andExpect를 통해 검증한다.
뿐만 아니라, DB값이 아닌,return되는 값을 통해 검증한다.
get에서 return되는 값은json 형식을 가지고 있기 때문에jsonPath를 통해 key, value를 검증한다.
ex ) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.name").value("martin"))은
**key 인("$.name") : **return된 객체의 name속성 **value인****.value("martin")) :** name 속성의 값으로 예측되는 테스트 값** ex 2) .andExpect(jsonPath("$.hobby").isEmpty())**은
**.isEmpty() :**value가 비어있다.@SpringBootTest 란?
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)스프링관련 기능을 사용해서 테스트를 진행한다는 의미이다.
@AutoWired 을 사용해 각 상황의 타입에 맞는 IoC컨테이너 안에 존재하는 Bean을 자동으로 주입한다.
** Service **
PersonService
- @Autowired Repository를 통해 repository의 method를 이용
- DAO클래스를 통해 DB연동을 처리한다.
- DAO로 DB에 접근하고 DTO로 데이터를 전달받은 다음, 비지니스 로직을 처리해 적절한 데이터를 반환한다.
@Slf4j @Service public class PersonService { @Autowired private PersonRepository personRepository; @Transactional(readOnly = true) public Person getPerson(Long id) { return personRepository.findById(id).orElse(null); } @Transactional public void postPerson(PersonDto personDto) { Person person = new Person(); person.set(personDto); person.setName(personDto.getName()); personRepository.save(person); } @Transactional public void modify(Long id, PersonDto personDto) { Person person = personRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow(PersonNotFoundException::new); if (!person.getName().equals(personDto.getName())) { throw new RenameIsNotPermittedException(); } person.set(personDto); personRepository.save(person); } @Transactional public void modify(Long id, String name) { Person person = personRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow(PersonNotFoundException::new); person.setName(name); personRepository.save(person); } @Transactional public void delete(Long id) { Person person = personRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow(PersonNotFoundException::new); person.setDeleted(true); personRepository.save(person); } }PersonServiceTest
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class) class PersonServiceTest { @InjectMocks private PersonService personService; @Mock private PersonRepository personRepository; @Test void getPerson(){ when(personRepository.findById(1L)) .thenReturn(Optional.of(new Person("martin"))); Person person = personService.getPerson(1L); assertThat(person.getName()).isEqualTo("martin"); } @Test void postPerson(){ personService.postPerson(mockPersonDto()); verify(personRepository, times(1)).save(argThat(new IsPersonWillBeInserted())); } @Test void modify() { when(personRepository.findById(1L)) .thenReturn(Optional.of(new Person("aonee"))); personService.modify(1L, mockPersonDto()); verify(personRepository, times(1)).save(argThat(new IsPersonWillBeUpdated())); } @Test void modifyByNameIfPersonNotFound() { when(personRepository.findById(1L)) .thenReturn(Optional.empty()); assertThrows(PersonNotFoundException.class, () -> personService.modify(1L, "daniel")); } @Test void modifyByName(){ when(personRepository.findById(1L)) .thenReturn(Optional.of(new Person("martin"))); personService.modify(1L, "daniel"); verify(personRepository, times(1)).save(argThat(new IsNameWillBeUpdated())); } @Test void delete(){ when(personRepository.findById(1L)) .thenReturn(Optional.of(new Person("martin"))); personService.delete(1L); verify(personRepository, times(1)).save(argThat(new IsPersonWillBeDeleted())); } private PersonDto mockPersonDto() { return PersonDto.of("aonee", "programming", "seoul", LocalDate.now(), "programmer", "010-1111-2222"); } }build.gradle 에 해당 코드 추가
testImplementation 'org.mockito:mockito-junit-jupiter'- Mock 테스트 개념 정리
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class))
Spring이 아닌 Mockito관련 기능을 사용해서 테스트를 진행한다는 의미이다.
그리고 이제는MockitoExtension)을 사용하고 더이상 스프링 컨텍스트는 사용하지 않기 때문에
@AutoWired는 아무런 동작을 하지 않는다.
대신,@InjectMocks는 테스트의 대상이 되는 클래스에 붙여주면 된다.
@Mock는 테스트의 대상이 되는 클래스에서@AutoWired 하고 있는 클래스에 붙여주면 된다.
그러면@Mock 이 붙은 클래스를 Mock으로 만들어서@InjectMocks 클래스에 주입해준다.
기존에 Spring context를 사용할 때는 data.sql을 통해 DB에 들어있는 값을 조회했던 것과 달리
@Mock 에는 빈껍데기로 아무런 동작을 하지 않는다. 따라서, 테스트를 위해서는 직접 지정해줘야 한다.
(EX)
when(personRepository.findByName("martin"))
.thenReturn(Lists.newArrayList(new Person("martin")));when ?
if와 같은 의미. 만약(personRepository.findByName("martin"))호출되면 (실제 호출이 아닌 가정이다.)
thenReturn ?
Lists.newArrayList(new Person("martin") 리턴한다
@SpringBootTest로 만들었다면 각 테스트케이스에 맞는 DB 데이터로 만들었어야한다.
그러나 Mock Test를 통해 보다 간단하게 구현할 수 있었다.
분기문이 많이 나오는 로직일 수록@SpringBootTest 적용하기 더 힘들다.
- Mock 테스트에서 정확하게 검증하는 방법
1.
verify는 post와 같이 return값이 void인 경우에 사용한다.
verify를 사용하지 않을 경우, 올바르게 테스트되었는지 검증할 수 없다.
verify(personRepository, times(1)).save(argThat(new IsPersonWillBeInserted()));
2.
PersonService에서
@Transactional
public voidmodify(Long id,String name) {
Person person =personRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow(PersonNotFoundException::new);person.setName(name)**;**
personRepository.save(person);
}person.setName(name)**;**해당 코드는 없어서는 안될 핵심 역할을 하는 코드이다.
그런데, 주석처리를 해도 test가 통과한다. 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해
PersonServiceTest에IsPersonWillBeUpdated 생성
private static class IsPersonWillBeUpdated implements ArgumentMatcher {
@Override
public boolean matches(Person person) {
return equals(person.getName(), "martin")
&& equals(person.getHobby(), "programming")
&& equals(person.getAddress(), "판교")
&& equals(person.getBirthday(), Birthday.of(LocalDate.now())))
&& equals(person.getJob(), "programmer")
&& equals(person.getPhoneNumber(), "010-1111-2222");
}private boolean **equals**(Object actual, Object expected) { return [expected.equals(actual);](expected.equals(actual);) } }PersonServiceTest의 modify 테스트에
verify(personRepository,times(1)).save(argThat(newIsPersonWillBeUpdated()));
이처럼 검증을 해주면 된다.
service - argumentmatcher
IsNameWillBeUpdated
public class IsNameWillBeUpdated implements ArgumentMatcher<Person> { @Override public boolean matches(Person person) { return person.getName().equals("daniel"); } }IsPersonWillBeDeleted
public class IsPersonWillBeDeleted implements ArgumentMatcher<Person> { @Override public boolean matches(Person person) { return person.isDeleted(); } }IsPersonWillBeInserted
public class IsPersonWillBeInserted implements ArgumentMatcher<Person> { @Override public boolean matches(Person person) { return equals(person.getName(), "aonee") && equals(person.getHobby(), "programming") && equals(person.getAddress(), "seoul") && equals(person.getBirthday(), Birthday.of(LocalDate.now())) && equals(person.getJob(), "programmer") && equals(person.getPhoneNumber(), "010-1111-2222"); } private boolean equals(Object actual, Object expected) { return expected.equals(actual); } }IsPersonWillBeUpdated
public class IsPersonWillBeUpdated implements ArgumentMatcher<Person> { @Override public boolean matches(Person person) { return equals(person.getName(), "aonee") && equals(person.getHobby(), "programming") && equals(person.getAddress(), "seoul") && equals(person.getBirthday(), Birthday.of(LocalDate.now())) && equals(person.getJob(), "programmer") && equals(person.getPhoneNumber(), "010-1111-2222"); } private boolean equals(Object actual, Object expected) { return expected.equals(actual); } }
*application.yml *
spring: jpa: show-sql: trueapplication.properties를 application.yml로 변경
why? 상대적으로 유연한 구조를 가졌기 때문
yml은 상위 계층에 대한 표현, List 등을 완전하게 표현할수가 있다. 또한, 최근의 많은 도구들이 yml 설정을 지원한다
test - resources - data.sql
@SpringBootTest 를 위해
insert into person(`id`, `name`, `year_of_birthday`, `month_of_birthday`, `day_of_birthday`) values (1, 'aonee', 1991, 8, 15); insert into person(`id`, `name`, `year_of_birthday`, `month_of_birthday`, `day_of_birthday`) values (2, 'david', 1992, 7, 21); insert into person(`id`, `name`, `year_of_birthday`, `month_of_birthday`, `day_of_birthday`) values (3, 'dennis', 1993, 10, 15); insert into person(`id`, `name`, `year_of_birthday`, `month_of_birthday`, `day_of_birthday`) values (4, 'sophia', 1994, 8, 31); insert into person(`id`, `name`, `year_of_birthday`, `month_of_birthday`, `day_of_birthday`) values (5, 'benny', 1995, 12, 23); insert into person(`id`, `name`, `year_of_birthday`, `month_of_birthday`, `day_of_birthday`, `job`, `hobby`, `phone_number`, `address`) values (6, 'tony', 1991, 7, 10, 'officer', 'reading', '010-2222-5555', 'seoul'); insert into person(`id`, `name`, `deleted`) values (7, 'andrew', true);
Exception
- dto
ErrorResponse
@Data @AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PRIVATE) public class ErrorResponse { private int code; private String message; public static ErrorResponse of(HttpStatus httpStatus, String message) { return new ErrorResponse(httpStatus.value(), message); } public static ErrorResponse of(HttpStatus httpStatus, FieldError fieldError) { if (fieldError == null) { return new ErrorResponse(httpStatus.value(), "invalid params"); } else { return new ErrorResponse(httpStatus.value(), fieldError.getDefaultMessage()); } } }PersonNotFoundException
@Slf4j public class PersonNotFoundException extends RuntimeException { private static final String MESSAGE = "Person Entity가 존재하지 않습니다"; public PersonNotFoundException() { super(MESSAGE); log.error(MESSAGE); } }RenameIsNotPermittedException
@Slf4j public class RenameIsNotPermittedException extends RuntimeException { private static final String MESSAGE = "이름 변경이 허용되지 않습니다"; public RenameIsNotPermittedException() { super(MESSAGE); log.error(MESSAGE); } }
**✔TEST 결과 확인 ( 모두 통과 ! 예 ! 에--! 🙋♀️ )**
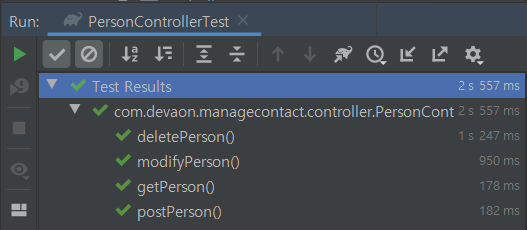
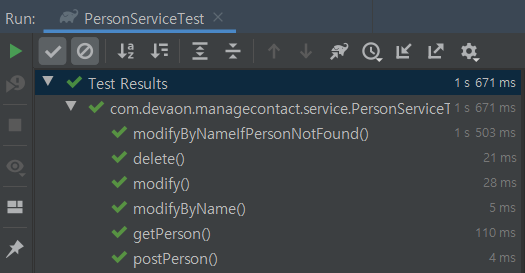
TDD (Test Driven Development 테스트 주도 개발 : 테스트가 개발을 이끌어 나간다 )
테스트 주도 개발을 함께 하려다 보니 신경 쓸 부분이 많아져 개발하는데 시간이 배로 걸렸다.
무엇보다 JPA 와 TDD를 처음 공부하다 보니 더욱 그랬던 것 같다.
직접 TDD를 해보니 개발을 하다 중요한 로직에서 취약한 실수가 있었다.자칫 모르고 넘어갈 수 있었던 문제였는데 테스트를 통해 바로잡을 수 있었다.
이를 통해, TDD의 중요성을 크게 느꼈다.
사실 처음에는 그저 내가 작성한 테스트가 통과되면 좋겠다는 생각으로 간략하게 작성했다.
그러나 나중에 보니 핵심로직에 제대로 된 검증을 하지 않고 있었다.
무용지물 한 테스트 코드를 작성하고 있었던 것이었다. (이럴거면 테스트 왜 해 🤦♀️)
이후로는 올바른 검증을 하는 테스트 코드를 작성하기 위해 노력했다.
올바르게 작동하는 깔끔한 코드를 만들기 위해 ! ! ! !
자연스럽게 TEST 코드를 작성하는 날이 올 때까지 꾸준히 공부해야겠다.반응형'Server > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
[Spring Security] JWT(JSON Web Token) 의 모든 것 (1) 2020.05.10 [spring boot] 스프링 부트와 AWS로 혼자 구현하는 웹 서비스-1 (0) 2020.05.03 [spring] TDD (테스트 주도 개발) 방법 (0) 2020.04.19 [Spring] jpa, Hibernate, mybatis 란? 그리고 SQL Mapper와 ORM (0) 2020.04.19 [Spring] 설정 및 구현 - 생명주기, MVC (0) 2020.04.12